Project Description
Market Need

The key objective in the management of this supply chain is to honour the warranty agreement with customers by making replacement parts available to conduct repairs within the agreed timeframes (e.g. Next Business Day, Same Business Day).
Having too much stock results in additional storage and obsolescence costs, while having too little stock results in stock out situations and poor customer service.

Technology Solution
The optimisation of a repair supply chain network involves two sub-problems that are related to the expected demand: capacity and inventory sub- problems. These sub-problems require companies to make decisions under uncertainty. The first decision deals with cost effective capacity planning for the expected work load. The second decision sets the appropriate inventory level subject to a given Service Level Agreement.
The TAC SCM simulator was designed to capture many of the challenges involved in supporting such dynamic supply chain decisions. A TAC SCM simulation consists of a number of “days” where personal computer (PC) assembly agents compete for customer orders and for procurement of a variety of components. The simulation includes entities such as component suppliers, factory assembly line scheduling etc. Customers issue requests for quotes and select from quotes submitted by the agents, based on delivery dates and prices.

A repair infrastructure is layered over the TAC SCM simulator, which provides real-time repair supply chain events to the analytics engine. The engine finds correlations among these events and builds a model of the repair requirements for each product and its components.
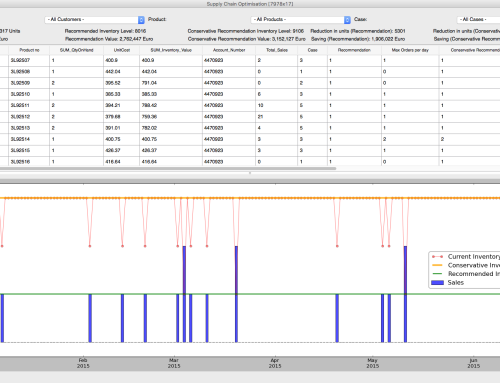
This model is used in repair capacity planning to optimise the use of staff and other resources to minimise costs and provide maximum quality of service for an expected repair demand. The system generates a resource and inventory capacity plan for a time period given constraints such as:
Many components can be ordered in bulk to minimise costs.
Lead time and delivery time are required to order a new component.
Many components can be replaced by similar components that may already be in stock.
Research Team
- Barry O’Sullivan
- Derek Bridge
- Ken Brown
- Paul Davern
- Liam O’Toole